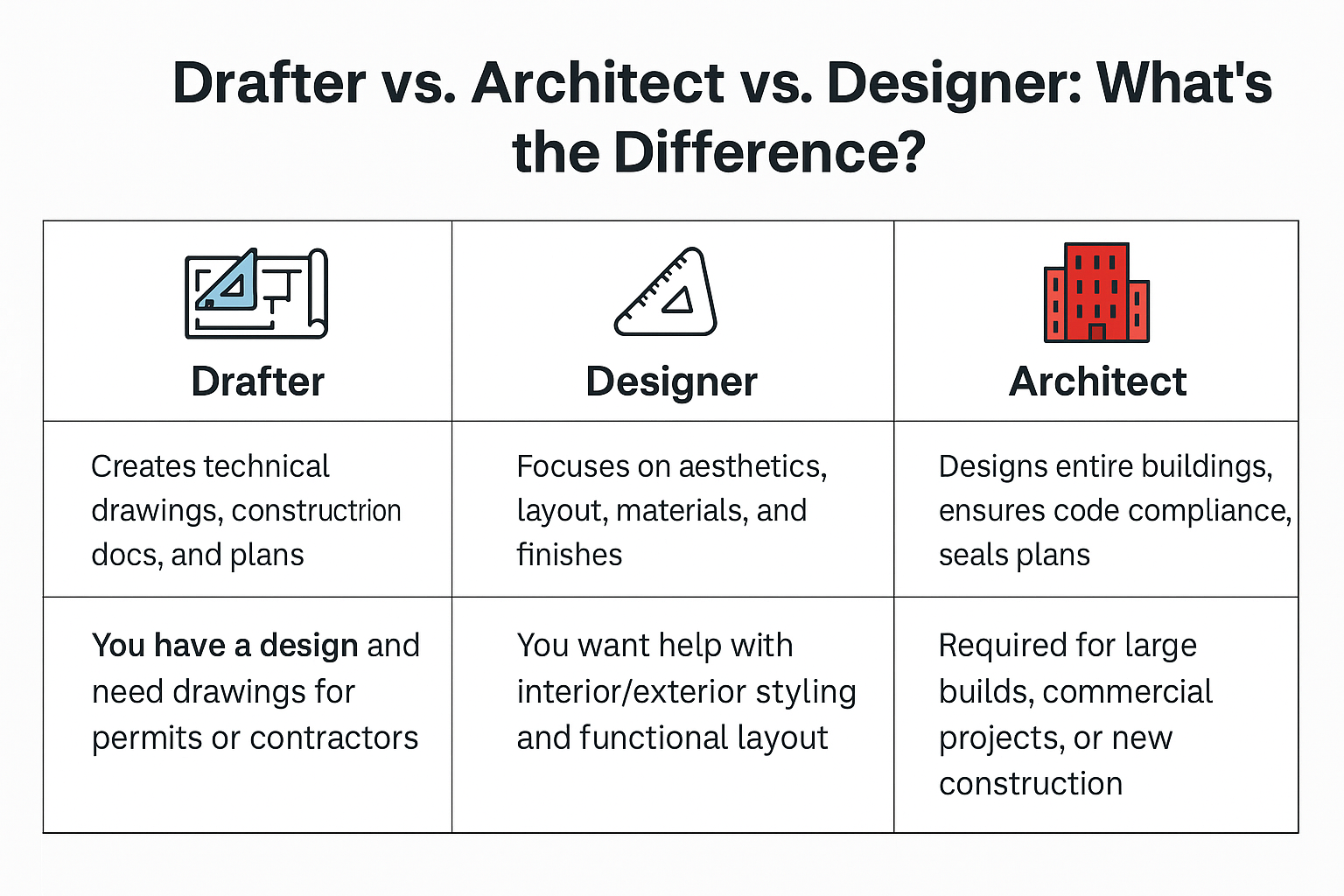
Unveiling the Dimensions of BIM: From 1D to 10D
Building Information Modeling (BIM) is a digital representation of the physical and functional characteristics of a facility. It serves as a shared knowledge resource for information about a facility, forming a reliable basis for decisions during its lifecycle from inception onward. The concept of BIM dimensions extends beyond the traditional 3D models, incorporating time, cost, sustainability, and more, to enhance project outcomes and efficiency.
Understanding these dimensions is crucial as they provide a comprehensive framework for managing the complexities of modern construction projects. While 3D BIM is widely adopted, the additional dimensions offer deeper insights and control, enabling more effective collaboration and decision-making across various sectors and regions.
BIM Dimensions Breakdown
- 1D – Conceptual Idea: Initiates with the project’s vision, focusing on needs analysis and feasibility studies.
- 2D – Drafting: Involves creating detailed technical drawings and plans essential for project approval and execution.
- 3D – Geometric Modeling: Develops a comprehensive visual model for design coordination and conflict resolution.
- 4D – Scheduling (Time): Integrates time-related data to simulate construction phases and optimize project timelines.
- 5D – Cost Estimation: Combines material quantities with financial data to forecast project budgets accurately.
- 6D – Sustainability / Energy Analysis: Assesses environmental impacts and energy efficiency to meet green building standards.
- 7D – Facility & Asset Management: Focuses on post-construction management, including equipment tracking and maintenance scheduling.
- 8D – Safety Planning: Enhances site safety through risk assessments and virtual training simulations.
- 9D – Lean Construction: Aims to streamline processes, reduce waste, and improve overall project efficiency.
- 10D – Lifecycle Automation / Industrialized Construction: Embraces smart technologies for real-time monitoring and prefabrication, integrating IoT and digital twins.
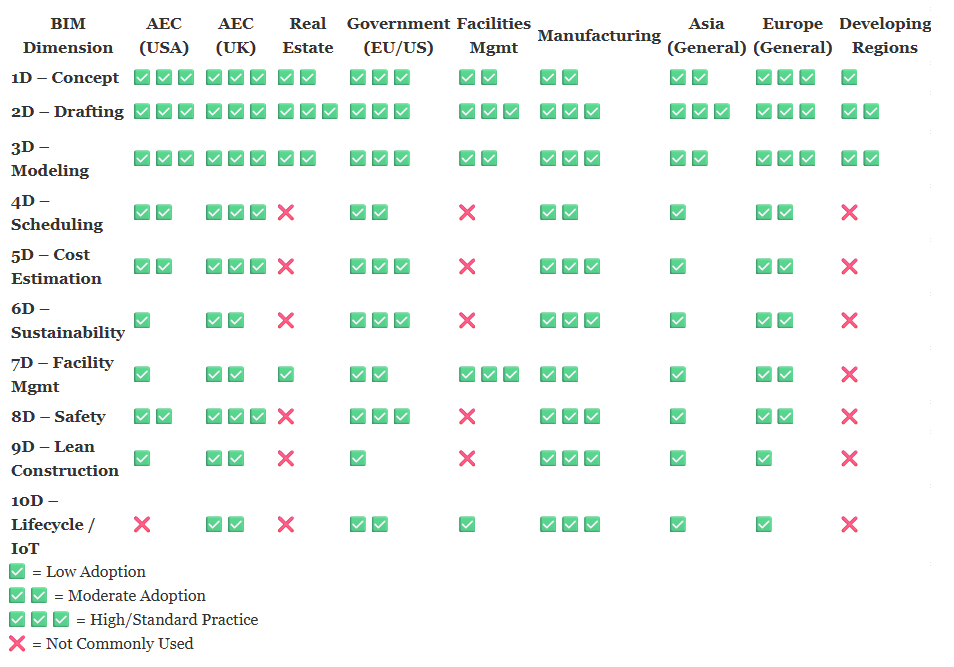
Global BIM Adoption
Understanding Regional and Sectoral BIM Variations
BIM adoption showcases a fascinating spectrum across various countries and sectors, shaped by unique regulatory frameworks and industry demands. In the UK and Nordic regions, government initiatives propel the utilization of advanced BIM levels, frequently reaching 5D and beyond. The U.S. AEC industry stands out as a frontrunner in 3D to 5D applications, yet it struggles to fully embrace the concept of lifecycle BIM. In the realm of facilities management, there’s a growing trend towards 7D BIM, which integrates time and cost management into the operational phase, enhancing the overall efficiency of building management. Meanwhile, the real estate sector often remains anchored in 2D and 3D due to a slower pace of digital transformation. Developing nations are making impressive strides by skipping traditional stages and adopting mobile-ready solutions for digital twins. The manufacturing and industrial sectors are progressively incorporating 9D and 10D BIM to boost innovation and operational efficiency. Public infrastructure projects frequently lead the way in adopting higher-dimensional BIM, backed by significant funding and supportive policies.
Looking forward, the infusion of artificial intelligence and machine learning into BIM practices is set to transform project management, enabling predictive analytics and more informed decision-making. This transformation will not only optimize workflows but also cultivate a culture of ongoing improvement throughout the construction industry, ensuring that all stakeholders can respond effectively to the evolving challenges of the market.
Real-World Usage and Constraints
Exploring Practical BIM Applications and Challenges
Embrace the Future of BIM with CAD Construct
The long-term value of adopting a full-spectrum BIM approach is transformative, offering unparalleled insights and efficiencies across the building lifecycle. By leveraging dimensional data, firms can revolutionize their workflows, from design and construction to maintenance and beyond. As the industry evolves, embracing advanced BIM dimensions becomes crucial for staying competitive and innovative. We invite you to explore how CAD Construct’s expertise in 3D scanning, visualization, and digital twin development can help you harness the full potential of BIM, driving your projects towards success.
References
- UK BIM Framework – Centre for Digital Built Britain
https://www.ukbimframework.org
→ Used to define standardized BIM dimensions (especially 3D–7D) and understand UK adoption. - National Institute of Building Sciences (NIBS) – National BIM Standard – US
https://www.nationalbimstandard.org
→ Referenced for U.S.-based definitions and industry-specific usage of BIM dimensions. - Autodesk Knowledge Network – BIM Dimensions Explained
https://knowledge.autodesk.com
→ Source for clear interpretation of 4D–7D applications in architecture and construction. - Dodge Data & Analytics – The Business Value of BIM in North America (SmartMarket Report)
https://www.construction.com
→ Provided adoption trends across AEC sectors in the U.S. and Canada. - McKinsey & Company – The Next Normal in Construction Report
https://www.mckinsey.com
→ Used for insight into global trends and emerging adoption in developing markets. - buildingSMART International – BIM Implementation Around the World
https://www.buildingsmart.org
→ Informed comparative global adoption rates, including Asia, Europe, and government initiatives. - ISO 19650 Framework for BIM
https://www.iso.org/standard/68078.html
→ Provided structure for information management and higher BIM dimensions.